Advanced Windows 11 tips: Task Manager
YOU’LL NEED THIS
ANY WINDOWS PC Process Explorer (https:// docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ sysinternals/downloads/ process-explorer)
IN THIS FIRST TUTORIAL in a new series showcasing how to get more from your Windows 11 setup, we’re starting with a detailed look at what’s going on under the hood of your machine. You may not currently care that, behind the scenes, your Windows installation is performing a complicated juggling routine involving a tangled web of applications, services, processes, threads, and handles, but we suspect that outlook will change the moment your system starts to slow down, become non-responsive, or prone to crashing.
Knowledge is power, and there are two primary tools that can help you peer behind the scenes to determine what’s going on, identify areas of concern, and even in some cases, restore non-responsive applications to life without force-quitting them and losing hours of unsaved work. The first, Task Manager, is built into Windows itself and has all the tools you need to resolve most problems, but if you need an even deeper dive into your PC’s software innards, then Process Explorer is the tool for you.
Armed with these tools, you’ll discover how to monitor and free up system resources, track down troublesome processes, and generally keep your PC running a bit more smoothly. So, without further ado, let’s pull back the curtain…
– NICK PEERS
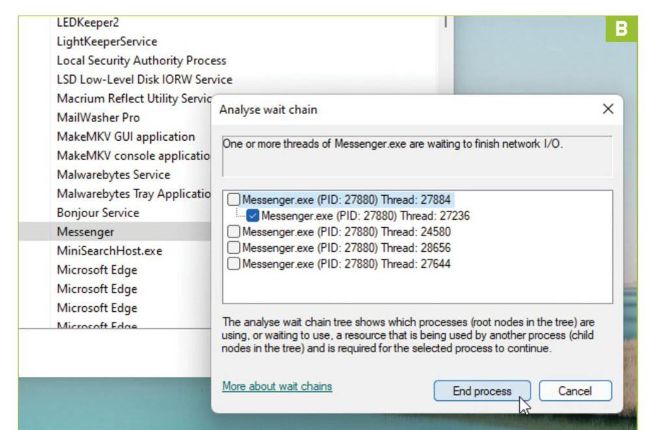
1QUICK-FIRE ORIENTATION
Let’s start with a quick tour of Task Manager’s key features. Step one is opening it—the quickest way is to learn a new three-fingered salute if you haven’t already: Ctrl + Shift + Esc (save Ctrl + Alt + Delete for times when Windows won’t respond). You can also access Task Manager in Windows 10 by rightclicking the Taskbar, or in Windows 11 by right-clicking the Start button and choosing Task Manager.
>> The basic Task Manager view is a simple list of running apps, so in the unlikely event you haven’t already gone beyond this, click ‘More details’ to access a more reassuringly packed seventabbed dialog packed with useful info. The annotation provides a quick overview of what each section does, but let’s take a deep dive and see what each section can provide in terms of useful diagnostic info and troubleshooting tools.
© MICROSOFT
2SEE WHAT’S RUNNING
The Processes tab is where you’ll get a detailed overview of what’s running on your PC. It’s split into three sections: Apps lists the programs you’ve launched via File Explorer—to see what processes each app is running, click the > next to its entry to expand the list. In most cases, there may only be a single process listed, or you may simply see multiple threads with the same name as the app itself, but others may provide more useful details. For example, Word will display a separate entry for each document you’ve opened, while Microsoft Edge goes even further in identifying each separate subprocess [Image A].