The Great Lakes – Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie and Ontario – are five freshwater giants that dominate the US landscape and cross over the Canadian border. Standing on their shores, you could be forgiven for thinking you were looking out to sea. These vast bodies of water have a collective volume of 6 quadrillion gallons. That’s more than one-fifth of the world’s total freshwater. The lakes provide drinking water to more than 40 million people, crucial shipping routes for more than 800 ocean vessels, granting them access to the continent’s interior, and sustain a rich ecosystem for fishing and agricultural practices.
Did you know?
Lake Michigan is the only lake entirely in the US
Did you know?
Lake Michigan is the only lake entirely in the US
Covering an area of 94,250 square miles, the Great Lakes are deserving of their name. They span across eight US states and two Canadian provinces. Among the five lies the world’s largest lake by surface area, Lake Superior, and the largest freshwater sand dunes, which line the shores of Lake Michigan. These are called the Sleeping Bear Dunes and rise 137 metres above the lake’s surface. The Great Lakes’ value supports wildlife, the national economy and the environment. They only exist because a million years of tectonic activity, glacial carving and rising temperatures forged them into the awe-inspiring geographical features we see today.
MAKING LAKES ON PLATES
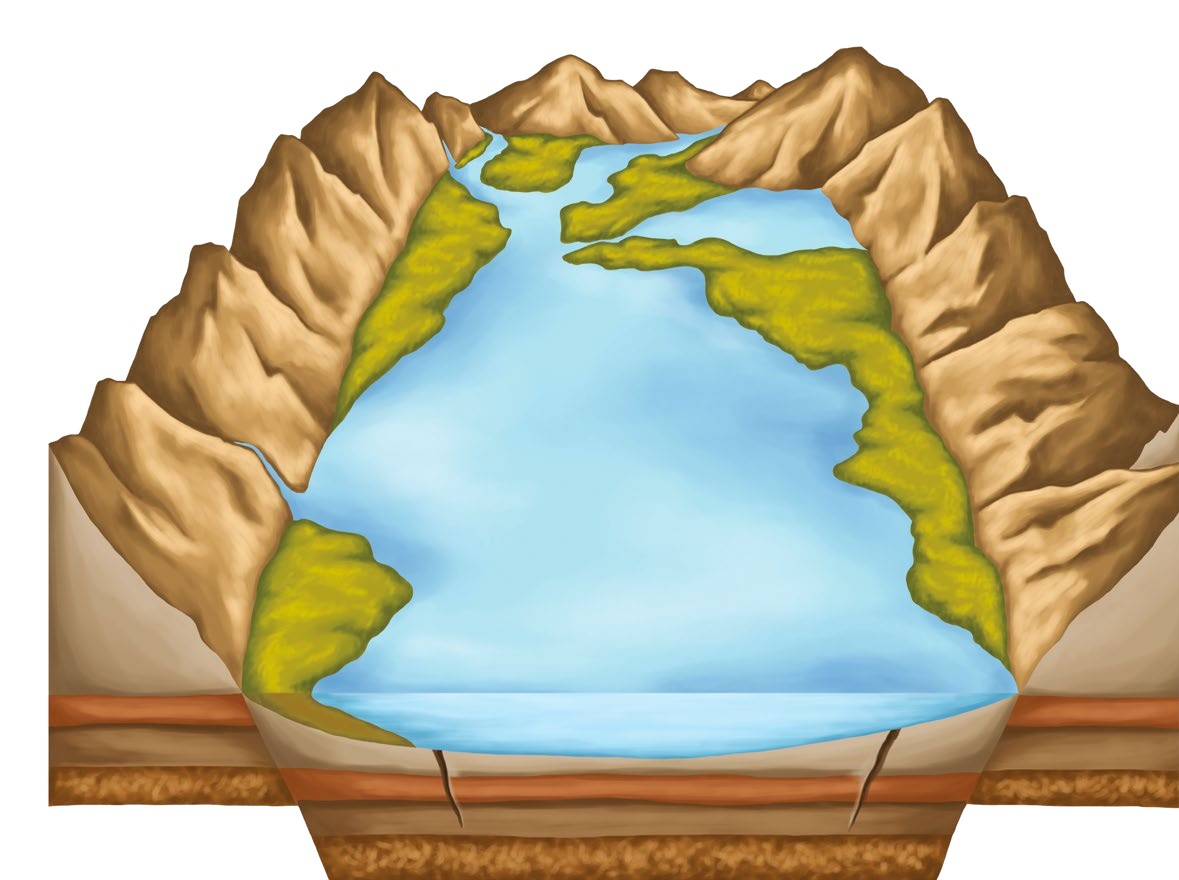
Tectonic plates can shift, creating a large basin in the land for a lake to form in
© Shutterstock
Tectonic plates are large pieces of the planet’s outer crust, called the lithosphere. Under the intense heat emitted at Earth’s core, these plates are slowly shifting and changing the shape of features on the surface. When two of these plates pull apart, they can create large cracks in the crust called rift valleys. Over time, these can fill up with water and become a lake. Plate tectonics can also form lakes via plates sinking to form basins for lakes to form in, or plates pushing against each other and creating cracks in the crust.
Tectonic plates can be responsible for forming large bodies of water, although they’re not the only way. For example, smaller oxbow lakes can form when part of a meandering river gets cut off into a separate body of water.
Tectonic plates are large pieces of the planet’s outer crust, called the lithosphere. Under the intense heat emitted at Earth’s core, these plates are slowly shifting and changing the shape of features on the surface. When two of these plates pull apart, they can create large cracks in the crust called rift valleys. Over time, these can fill up with water and become a lake. Plate tectonics can also form lakes via plates sinking to form basins for lakes to form in, or plates pushing against each other and creating cracks in the crust.
Tectonic plates can be responsible for forming large bodies of water, although they’re not the only way. For example, smaller oxbow lakes can form when part of a meandering river gets cut off into a separate body of water.
THE FIVE GIANTS