Database
Rediscover speed with the Redis revolution
REDIS
Mark Chisholm shows off Redis’s database as a powerful and versatile caching solution, focusing on its speed and performance benefits.
Credit: https://redis.io
Redis
is an open-source, in-memory data structure store that has gained popularity R as a highly efficient caching and messaging system. It prioritises speed, efficiency and versatility, making it a top choice for various applications. Redis’s ability to store and manipulate data structures directly in memory sets it apart from traditional key-value stores, enabling complex operations and algorithms.
OUR EXPERT
Mark Chisholm is a technology enthusiast and programmer. He has a passion for exploring emerging database trends and technologies, sharing their findings through informative articles.
QUICK TIP
Get the code from the Archive: www. linuxformat. com/archives? issue=305 or direct from Mark’s Git: https://github. com/MarkCb3d/redislxf305
With exceptional performance due to its in-memory nature, Redis delivers rapid read and write operations for low-latency access to frequently accessed data. It powers real-time applications, offers task queue capabilities, supports geospatial indexing, and more. By bypassing disk I/O operations, Redis achieves reduced latency and improved throughput. But considerations include sufficient memory and data volatility.
Redis provides persistence mechanisms through snapshotting and append-only file (AOF) persistence, offering options for data durability and recovery. Atomic operations ensure consistency and prevent race conditions in concurrent environments.
Installation:
First, check that the hardware requirements can be suitably met for your Redis install. The recommended requirements are at least two nodes (these could be virtual machines) with 10GB or more of RAM and 20GB or more of disk space. Fortunately, most major Linux distributions provide packages for Redis.
It’s worth noting that if you’re using a very minimal OS (like a Docker container), it’s recommended that you install Lsb-release, Curl and Gpg before Redis. This can be done with the following on Ubuntu/Debian:
With that step done ,we need to add the repo to Apt, update and install it:
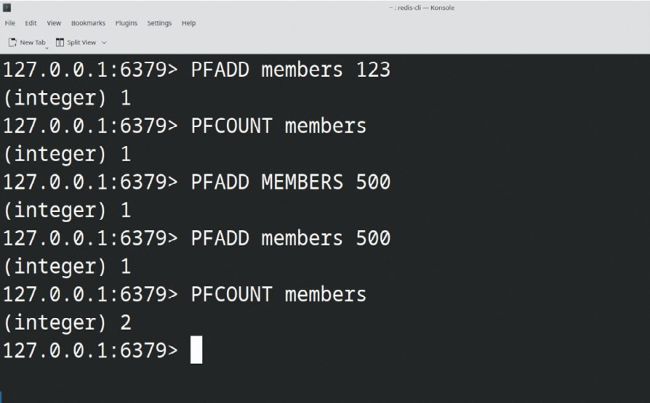
The Redis HyperLogLog is a probabilistic data structure that estimates the cardinality of large data sets with high accuracy using memory.
Alternatively, Redis is available from the Snap store with the command: